Consider the following example
declare @gender char(1)
set @gender ='M'
select case when @gender ='M' then 'Male' else 'Female' end as gender
The above t-sql code checks if @gender is 'M', return 'Male' else 'Female'
The same can be done using IIF as shown below
declare @gender char(1)
set @gender ='M'
select iif(@gender ='M','Male','Female')
You can also use IIF while selecting rows from a table column as shown below
create table #t(emp_id int, emp_name varchar(100),gender char(1), grade int)
GO
insert into #t(emp_id,emp_name, gender,grade)
select 1,'Suresh','M',1 union all
select 2,'Ramesh','M',3 union all
select 3,'Neela','F',2 union all
select 4,'Magesh','M',2 union all
select 5,'Sara','F',1
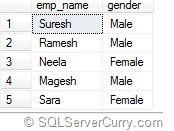
select emp_name,IIF(gender='M','Male','Female') as gender from #t
The CHOOSE function chooses the value from a list based on the ordinal position. If the value is 1, it chooses the first value, if it is 5, it chooses 5th value and so on from the list
The following can be used to illustrate what CHOOSE does
select emp_name,grade,CHOOSE(grade,'Manager','Project Leader','Developer') as grade_desc from #t

Based on the value available for the grade, it chooses between a 'Manager', 'Project Leader' or a 'Developer'
Both these expressions can be used to reduce the amount of code written using CASE expression

No comments:
Post a Comment